
When it comes to connecting our devices to the Internet, IP addresses play an important role. There are two main types of IP addresses: IPv4 and IPv6. But what’s the difference between the two and why should we deal with it sooner rather than later? Let’s take a closer look at what IPv4 and v6 are and what advantages and disadvantages you can expect with them – IPv4 vs IPv6.
IPv4 vs IPv6
IPv4 (Internet Protocol Version 4) is the older of the two IP address types and was introduced back in 1983 and has been in use since the ARPANET of that time. It allows for the assignment of up to 4.3 billion unique IP addresses on the World Wide Web, or the public portion of the Internet. This may sound like a large number, but with the increasing proliferation of Internet-enabled devices such as smartphones, tablets and smart home devices, the number of IP addresses still available is becoming ever scarcer. Still, this is currently less of a threat than you might think. After all, you usually only use a single IP address on the public WWW. Your devices themselves are located in the private LAN and occupy only one private IP, such as 192.168.0.xxx. This type of private addresses can be assigned by any router or DHCP server without further ado. Public addresses are not occupied for this purpose.
IPv6 (Internet Protocol Version 6) is the younger of the two types, was standardized in 1995 and first introduced in 1998. It allows the assignment of 340 sextillion unique IP addresses. This unimaginably large number is intended to ensure that sufficient IP addresses will be available for all devices and applications on the Internet in the distant future.
The differences between IPv4 and IPv6
One of the most obvious differences between version 4 and 6 is the number of IP addresses available. As mentioned earlier, IPv4 allows the allocation of up to 4.3 billion IP addresses, while IPv6 allows the allocation of 340 sextillion IP addresses. Another difference is the length of the IP addresses. IPv4 addresses consist of 32 bits and are represented in the form xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx. It is still relatively easy to enter such an address manually. IPv6, however, takes the cake in terms of length. These addresses consist of 128 bits and are represented in the form xxxx:xxxx:xxxx:xxxx:xxxx:xxxx:xxxx. Not only digits are possible, but sometimes also HEX values, i.e. all characters from a to f as well as digits from 0 to 9.
Do you prefer IPv4 instead of IPv6?
Both IPv4 and IPv6 are valid Internet protocols and are currently used equally. However, as the number of available IPv4 addresses becomes scarcer, IPv6 is increasingly seen as the future of the Internet, although the transition may take several more years. Since both types exist simultaneously, the transition is smooth. As an end user, however, it doesn’t really matter to you which protocol you use on the WWW.
Although IPv6 is the newer and more future-proof option, IPv4 is still widely used. Many older devices and networks only support IPv4 and it can be difficult to switch them to IPv6. However, it is important to note that IPv4 addresses are becoming scarce and it may become increasingly difficult to obtain new IPv4 addresses in the future. Therefore, it is recommended that you support both IPv4 and 6 and gradually migrate to IPv6. If your provider already provides v6, you can of course already use the new standard.
IPv4 and IPv6 at the same time on a Fritzbox
Many modern routers and networks, such as the Fritzbox, support both standards – IPv4 and IPv6. This means that both IPv4 addresses and IPv6 addresses can be assigned when setting up the Fritzbox, and consequently both variants can be used. However, this also implies that you have to activate or deactivate the desired standards in your Windows 10 or 11 network settings. If both are active at the same time, all traffic runs over v6.
Advantages and disadvantages
Both protocols offer very specific advantages and disadvantages, so even using both standards at the same time is often the more sensible solution. IPv4 has the advantage of being widespread and widely supported, while IPv6 has the advantage of having more addresses available and is generally easier to manage. However, IPv4 has the disadvantage that the number of available addresses is very limited compared to v6, while IPv6 has the disadvantage that it may not be supported by older devices and networks.
Is IPv6 faster than IPv4?
Although IPv6 offers greater functionality and enhanced capabilities, it does not offer an advantage over IPv4 in terms of speed. It rather depends on other factors like the speed of your internet connection and the performance of your internal network. IPv6 vs IPv4 performance therefore turns out to be pretty much identical. Both protocols are capable of transmitting data quickly and in packets. However, a major advantage of IPv6 is its support for a larger number of devices and easier address management.
Convert Internet Protocol
One way to convert IPv6 traffic to IPv4 is to use so-called tunneling technologies. An IPv6-over-4 tunnel, or IPv4 to IPv6 tunnel, allows IPv6 packets to travel through an IPv4 network by embedding the v6 data into IPv4 packets. This allows IPv6 endpoints to access IPv4 resources even if the IPv4 network does not have native IPv6 support. There exist a number of different tunneling protocols that can be used, such as Teredo, 6to4, or ISATAP. However, one disadvantage of tunneling technologies is that they can add overhead, affecting speed and latency.
Switching IPv6 to IPv4
Switching from IPv6 to the older IPv4 protocol, also known as a downgrade, may be necessary for a number of reasons. One common reason is that certain applications or devices are only compatible with IPv4 and therefore do not function as desired on an IPv6 network. Another reason may be that the IPv6 network is not running stably due to errors or problems, and therefore needs to be temporarily switched back to IPv4. To switch from IPv6 to 4, IPv6 support can be disabled on the router or network device, or special software can be used that allows tunneling IPv6 packets into IPv4 packets. It should be noted, however, that downgrading to IPv4 is not the optimal solution in the long run, as IPv4 addresses will become scarce and may not be sufficiently available in the future.
If you want to use a certain protocol in your Windows 10 or 11 or just want to see the current setting, you can easily do this via the network settings.
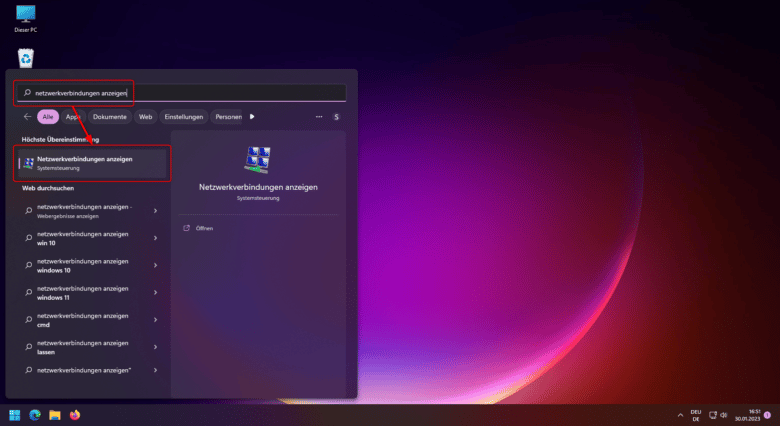
Search for “Show Network Connections” in the Start menu, click on it and then right-click on your currently used network connection. Select “Properties” to open another window with information about your selected connection.
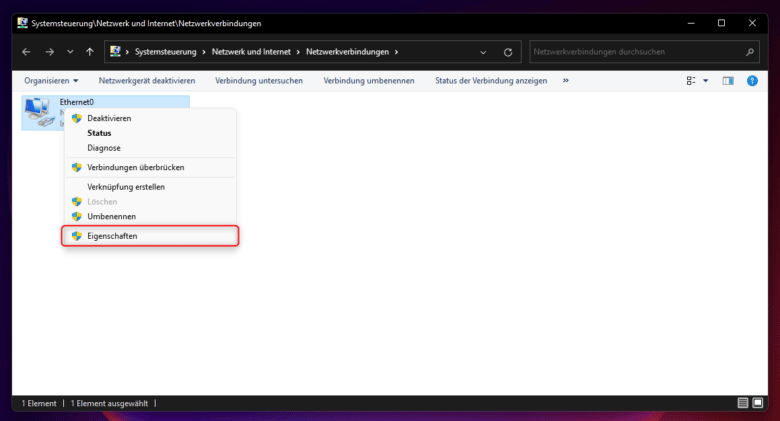
Now you can see in the list which protocols are enabled. In a standard Windows 11 installation, both protocols, i.e. v4 and v6 are already enabled at the same time. This leads not so seldom to problems in the network – especially in mixed environments. For example, computers do not appear in the network environment or open games in the LAN are not displayed because your game is not running on the same protocol as another computer.
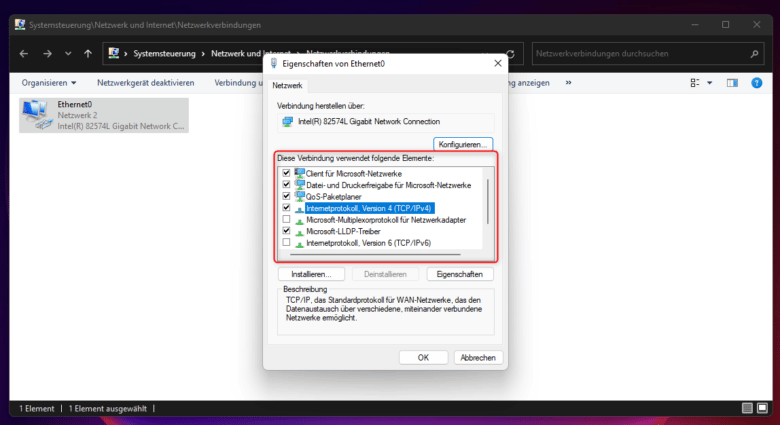
If you want to change this, you can simply check or uncheck the desired protocol. In the local network, for example, you will hardly be able to take advantage of IPv6. On the contrary, it is an efficient way to bypass all firewalls on your computer, especially those of third parties. So it may make sense to disable IPv6 and continue to use v4 on your LAN, since this standard is sufficient and you don’t have to enter long IP addresses.
Where is the journey going?
IPv4 vs IPv6 is an important topic, as Internet Protocol version 4 (IPv4) has been the primary method of identifying and connecting devices on the then ARPANET and today’s Internet, respectively, since its introduction in 1983. However, with the rapid growth of the Internet and the increasing number of devices online, IPv4 addresses are gradually becoming scarce. To solve this problem, Internet Protocol version 6 (IPv6) has been created.
IPv6 offers a much larger number of possible addresses, improving the efficiency and scalability of the Internet. Another important aspect when considering IPv4 vs IPv6 is also security, as IPv6 offers built-in support for security protocols such as IPSec. Overall, IPv6 offers a variety of advantages over IPv4, which is why it is important sooner rather than later that enterprises and organizations migrate their networks and devices to IPv6. In any case, communication and the networking of all devices remain the decisive factor for success in the digital world.




No replies yet
Neue Antworten laden...
Gehört zum Inventar
Beteilige dich an der Diskussion in der Basic Tutorials Community →